
Oral cavity anatomy with educational labeled structure vector illustration
Familiarity with the radiologic anatomy and landmarks of the floor of the mouth is helpful for detecting and characterizing pathologic processes that occur there and extend to deep tissues and beyond. A wide range of pathologic processes may involve the floor of the mouth, the part of the oral cavity that is located beneath the tongue.
Anatomical landmarks
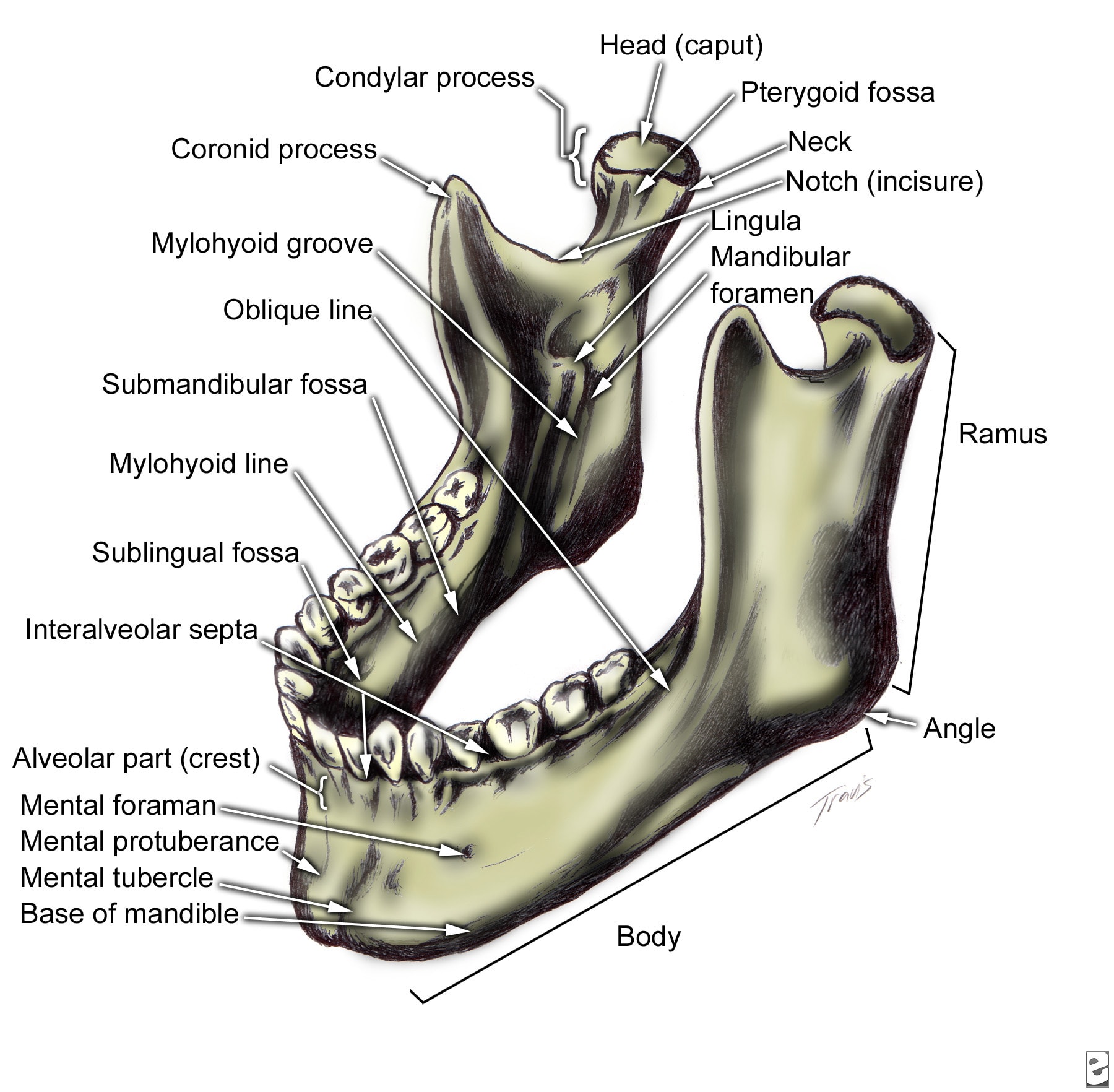
The base is the inferior part of the body that features several anatomical landmarks. On its external surface, we can identify: . The mandibular symphysis: Fibrous tissue in the midline of the mandibular body, which ossifies by the first year of life.It unites the left and right halves of the mandible in order to form a single, symmetrical bone. The mental protuberance: A bony prominence at.

Anatomic Landmarks Dentures Mouth
Hand: Anatomy, is a complex. Diagram of the mouth and lips showing their different components and landmarks. Image: "The mouth includes the lips, tongue, palate, gums, and teeth" by OpenStax College. License: CC BY 4.0 Movement. Numerous muscles are responsible for movement of the lips.
ORAL & MAXILLOFACIAL SURGERY Facial Bone Anatomy
The modiolus is the anatomical point at the corner of the mouth or angle of the mouth where the orbicularis oris, buccinator, caninus, triangularis, and zygomaticus muscles intersect and are located near the rim of the mouth (Fig. 6.44). It is also called as the fibromuscular condensation where the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles meet together.
ANATOMICAL LANDMARKS IN EDENTULOUS MOUTH Mind Map
Landmarks of the oral tissues include the palate, tongue, cheeks and floor of the mouth. It is significant to recognize the normal appearance of these structures during an intraoral examination of the patient. Fauces - Passageway from oral cavity to pharynx.

Mouth Teeth Diagram with Label coordstudenti
The stomatognathic system includes various anatomical structures, which allow the mouth to open, swallow, breathe, phonate, suck and perform different facial expressions. These structures are the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), jaw and mandible, muscle tissues and tendons, dental arches, salivary glands, as well as the hyoid bone and the muscles that connect the latter to the scapula and the.

Anatomical Landmarks of the Mouth EennHorton
Anatomy of the Oral Cavity Joe Iwanaga & R. Shane Tubbs Chapter First Online: 06 November 2021 1225 Accesses 1 Citations Abstract In this section, the surface structures of the oral cavity, which is necessary to understand the mimetic muscles and floor of the mouth, will be reviewed. Download chapter PDF 3.1 Surface Anatomy of the Oral Cavity

Facial landmarks divided into anatomical and pseudoanatomical... Download Scientific Diagram
1. Describe the basic anatomy of the ear, nose, mouth, and throat. 2. Perform a basic examination of the ear, nose, mouth, and throat, identifying normal and pathological conditions. 3. Properly use an otoscope to examine the ear and the nose. 4.

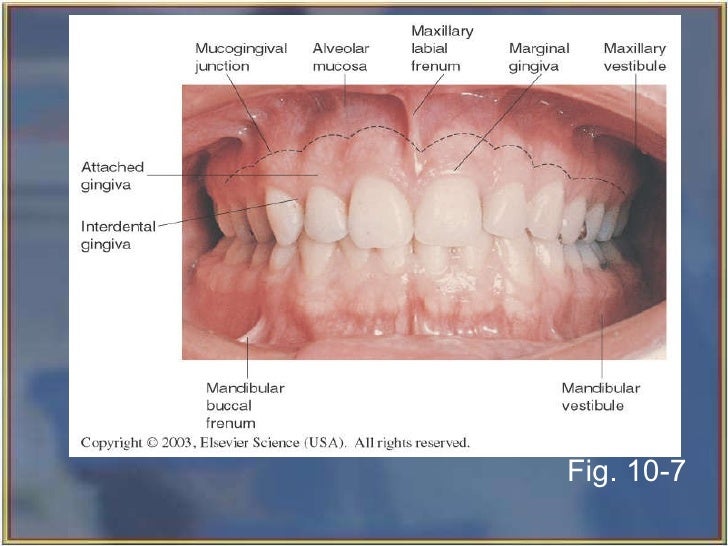
Maxillary Landmarks Labial frenum, Incisive papilla, Buccal frenum, Maxillary alveolar ridge
The tooth is one of the most individual and complex anatomical as well as histological structures in the body. The tissue composition of a tooth is only found within the oral cavity and is limited to the dental structures. Each tooth is paired within the same jaw, while the opposing jaw has teeth that are classified within the same category. However they are not grouped according to structure.

Surrounding Muscles of Upper Complete Denture. Dentistry, Dental hygiene student, Dental
The easiest anatomical landmark in the floor of the mouth examination, is the curvature of the tongue's surface. Also important is the determination of the air-tissue interface [3, 6]. Intraoral probes are more useful when we want to examine the tongues surface since they are easier to handle in such a small region.
landmarks of face and oral cavity
These landmarks also form a benchmark for determining normal facial anatomy when performing an extraoral examination on a patient. 1 Figure 2. Facial Landmarks. Ala - Wing of the nose. Inner canthus of the eye - The inner corner of the eye. Labial commissures - Corners of the mouth.

Anatomical Landmarks of the Mouth AmberaresKing
Revisions: 15 format_list_bulleted Contents add The oral cavity, better known as the mouth, is the start of the alimentary canal. It has three major functions: Digestion - receives food, preparing it for digestion in the stomach and small intestine. Communication - modifies the sound produced in the larynx to create a range of sounds.

Dentistry lectures for MFDS/MJDF/NBDE/ORE Anatomical Landmarks Of Panoramic Radiographs
The anatomical landmarks of the oral fissure and the lips in a 20-year-old female. Full size image. The lips (labialis, superioris,. It contributes to the modiolus of the mouth in addition to the other facial muscles contributing to the tendinous chiasm lying slightly superior to the lateral commissures of the oral fissure (Hur et al. 2010a, b).

Schematic drawing of the oral cavity [97]. Download Scientific Diagram
Normal Anatomic Landmarks of the Head Neck and Oral Cavity Bone Structure of the Face Facial Landmarks Landmarks in the Oral Cavity Teeth in the Oral Cavity Types of Teeth, Structures, Location and Functions Divisions and Components of the Teeth Types of Teeth and their Functions Surfaces of the Teeth Dentitions Primary Dentition

landmarks found in the oral cavity
The cavity is separated into anterior and posterior parts by the dental arches (or teeth): the anterior oral vestibule sits anteriorly to the teeth and behind the lips, whilst the oral cavity proper describes the area behind the teeth.

mandibular structures Radiographic Anatomy Pinterest Anatomy, Dental and Dental anatomy
The maxillary and mandibular edentulous soft tissue anatomy within the denture space of the oral environment is shown in Figure 1. Anatomical landmarks such as the retromolar pads, external oblique, mentalis muscle, frenum attachments, mylohyoid ridge, tuberosities, hamular notches, incisive papilla, labial sulcus, and buccal vestibule are.